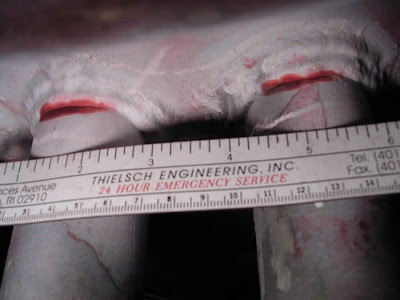
Liquid Penetrant Inspection (PT) is another common method of
NDT, and is solely used to detect surface breaking discontinuities, which are
free from debris that can limit the entrance of the dye (oil, grease and
paint). This method of Inspection can be applied to Ferromagnetic and
non-ferromagnetic materials, however it is most commonly used in
non-ferromagnetic components, for example when MT is not practical. The Liquid
Penetrants used have a low viscosity and a high affinity for metallic surfaces.
The dyes are applied to the test part by aerosol spray or by being submerged in
a tank were the dye penetrates any surface breaking flaws. After a required
soak time the dye can be removed so no excess fluid remains on the surface and
a thin coating of a highly absorbent developer is sprayed over the test area.
The developer draws any entrapped dye out of any cracks of fissures by
capillary action and the dye.
Liquid Penetrant Inspection requires the test object or
material to be thoroughly precleaned and free of paint, grease and loose
debris. The test area is then coated with a visible or fluorescent
dye solution which is allowed to "soak" into open surface flaws. After a suitable dwell time the excess dye is removed from
the surface and a developer which draws out the dye solution out of
imperfections open to the surface is applied. With visible dyes, the vivid
colour contrast between the penetrant and the developer is used to highlight
any flaws. With fluorescent dyes, an ultraviolet "black light" lamp
is used to contrast the "bleed out" and fluoresce brightly, allowing
the imperfection to be seen readily.
Penetrant inspection is a simple and very portable method of
flaw detection.
Materials that can be inspected using penetrant inspection
are:
- Aluminium
- Ceramics
- Stainless steel
- Glass
source : ndta.org.nz and eurondt.com
Liquid Penetrant Inspection (PT) is another common method of NDT, and is solely used to detect surface breaking discontinuities, which are free from debris that can limit the entrance of the dye (oil, grease and paint). GE USM Go
ReplyDelete